Experiential learning allows students to learn through hands-on experiences, including practical work, internship, volunteer work, and other real-world activities like project-based learning. The approach of experiential learning as been used as an educational technique for centuries and is used today in Higher Education to give students valuable knowledge and retained skills to serve them in their future careers.
Where it All Started: the History of Experiential Learning
What began as humble apprenticeships had the core of what makes experiential learning what it is today: human to human knowledge transfer by doing. The history of experiential learning is traced back to medieval universities where students would learn through hands-on experience in apprenticeships. And of course, informal learning by doing goes back further and is as old as humanities use of tools.
This more formal medieval approach was seen as a way for students to build practical knowledge and skills useful in their future jobs. During the Renaissance, experiential learning grew further as students studied a variety of subjects though hands-on experience including law, engineering and, of course, painting.
19th and 20th Century Experiential Learning
In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, experiential learning became more formalized in Higher Education. In the United States, John Dewey introduced the concept of “Experiential Education,” which emphasized the importance of hands-on learning and real-world experience in education. This approach was embraced by many universities that began integrating practical experiences into their educational programs.
In the mid-20th century, the popularity of experiential learning grew further. This was due, in part, to the rapid growth of the industrial and technological sectors which created new opportunities for students to gain hands-on experience in various fields. Additionaly, many schools began offering programs specifically focused on experiential learning which at the time generally meant co-op programs and internships. In 1974 Dr. David Kolb published the seminal book Toward an Applied Theory of Experiential Learning, marking the start of experiential learning theory and introducing modern academic rigor to the field.
Experiential Learning in the Modern Era
Today, experiential learning is an integral part of Higher Education and it is widely recognized as an effective way for students to learn valuable and career-ready skills. Many universities offer a range of experiential learning opportunities including internships, co-op programs and, more recently, project-based learning. These hands-on learning programs provide students with real-world experience in their field of study and valuable skills that will serve them in their future careers.
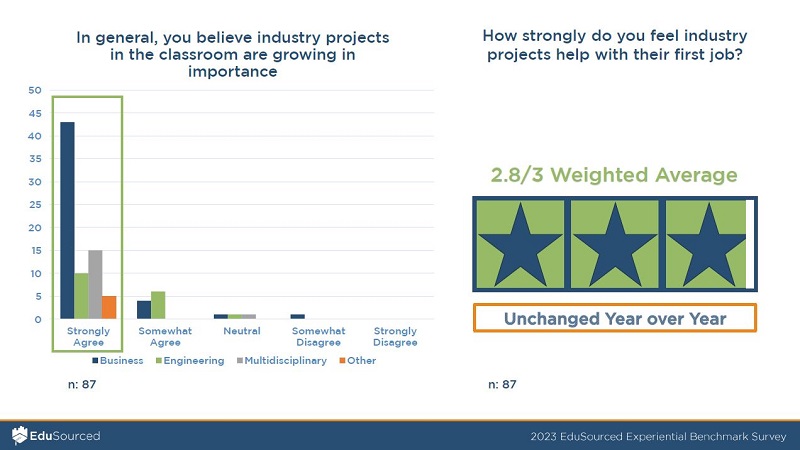
To this day, faculty and staff involved in experiential learning rate it as crucial to their students’ professional development as can be seen on page 26 of the 2023 EduSourced experiential learning benchmarking report.
The Future of Experiential Learning
An area of improvement for Experiential Learning, we believe, is adding mentors to supplement project teams and faculty oversight. Some schools are already doing this and to learn more about how cutting-edge Experiential Learning programs supplement their project teams with expert mentors from their communities, click here.
EduSourced is the most widely adopted software platform for managing experiential project-based learning, often referred to as capstone, senior design, practicum and project-based learning or PBL. To learn more, fill out the form below for a live demo.